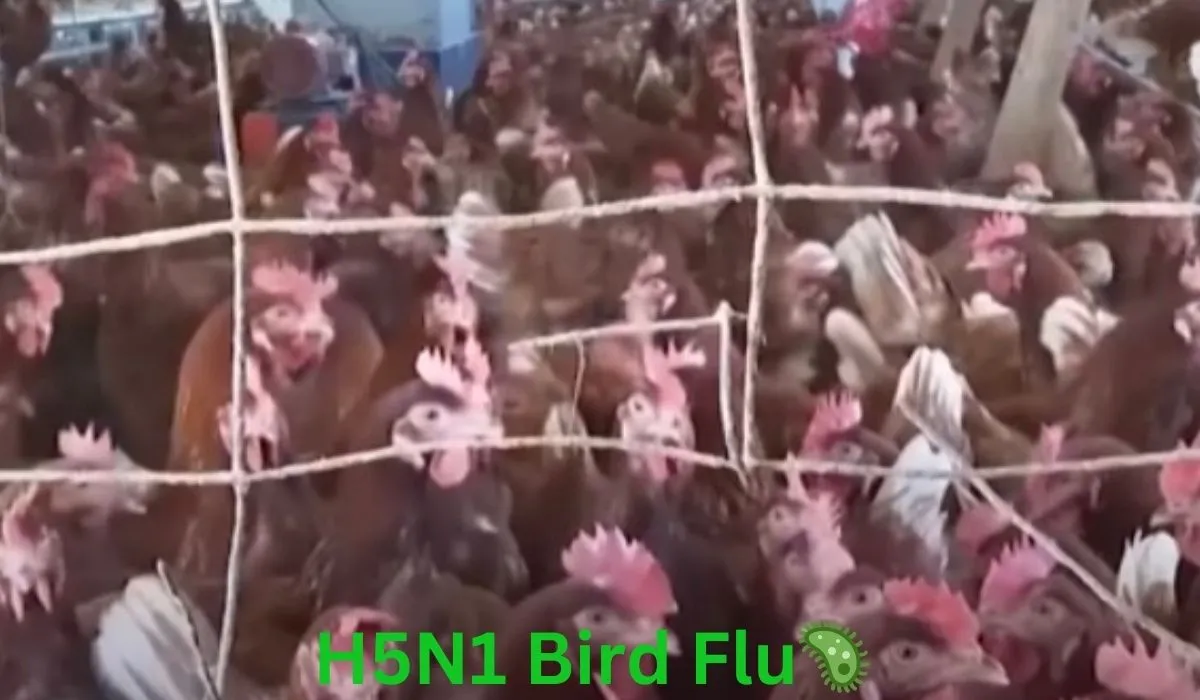
The H5N1 bird flu outbreak has resurfaced as a major health concern in the United States, with Louisiana recently confirming the first human death linked to the virus. While bird flu primarily affects poultry and wild birds, the potential for human transmission has raised serious questions among health officials. The news of the Louisiana bird flu death has sparked fears of a wider outbreak, especially as cases among birds and mammals continue to rise.
This article explores what H5N1 bird flu is, how it spreads, its symptoms, and what steps are being taken to prevent a larger health crisis. With flu season already in full swing, the presence of H5N1 in the U.S. demands urgent attention.
In The News
🦆 What is Bird Flu? Understanding the H5N1 Strain
Bird flu, also known as avian influenza, is a highly contagious viral infection that affects birds, particularly poultry and wild waterfowl. The H5N1 strain is one of the most dangerous forms of the virus because of its ability to infect mammals, including humans.
Unlike seasonal flu, which spreads rapidly from person to person, H5N1 bird flu transmission is mostly limited to those who have direct contact with infected birds. However, scientists warn that if the virus mutates, it could gain the ability to spread between humans, leading to a serious global health emergency.
📍 Louisiana Reports First Bird Flu Death: Why This Case Matters
Health officials in Louisiana have confirmed the first human fatality linked to bird flu in the United States. The individual was reportedly exposed to infected poultry, and despite medical intervention, the illness proved fatal.
This case is alarming because H5N1 has a high mortality rate in humans, even though human infections remain rare. The Louisiana Department of Health has assured the public that there is no immediate risk of widespread human transmission, but they are increasing surveillance efforts to prevent further infections.
🤒 Bird Flu Symptoms: What to Watch For

One of the challenges in detecting H5N1 bird flu in humans is that its symptoms closely resemble those of regular influenza. This similarity makes it difficult to diagnose early, which is why awareness is crucial.
Also Read:
- Alabama Nursing Student Triumphs: Jasmine Williams Crowned Miss America 2025
- Fox Sports Ex-Host Faces Lawsuit Over Harassment Allegations: $1.5M Offer for Sex Claimed by Hairstylist
- 🌟 Golden Globes 2025: A Night of Surprises, Star Power & Historic Wins 🎭✨
- Biden Honors Hillary Clinton, Michael J. Fox, and Denzel Washington with Presidential Medal of Freedom
- Steelers vs. Bengals: Biggest Winners and Losers in a Thrilling Clash
- Filmmaker Jeff Baena Dies by Suicide at 47: A Visionary Storyteller Lost Too Soon
- Solo Leveling Season 2: A Thrilling Return to the Shadow Monarch’s Rise
- Tiffany Stratton’s Victory: A Defining Moment in WWE Women’s Division
🛑 Common Symptoms of 🦠 H5N1 Bird Flu:
✅ High fever 🌡️
✅ Persistent cough 🤧
✅ Sore throat 👄
✅ Muscle aches 💪
✅ Shortness of breath 😤
✅ Fatigue 💤
✅ Conjunctivitis (red, irritated eyes) 👀
In more severe cases, H5N1 can cause pneumonia, respiratory failure, organ failure, and even death. The high fatality rate of bird flu in humans makes early detection and treatment extremely important.
If you have been in contact with birds, poultry farms, or live bird markets and experience flu-like symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
🦠 How Does H5N1 Bird Flu Spread?
Unlike human flu viruses, bird flu does not spread easily from person to person. Instead, it primarily transmits through direct contact with infected birds or their bodily fluids. However, scientists worry that mutations in the virus could change this.
🔬 Main Ways H5N1 is Transmitted:
➡️ Handling sick or dead birds 🐦
➡️ Coming into contact with bird droppings 💩
➡️ Exposure to contaminated surfaces 🏡
➡️ Consuming undercooked poultry or eggs 🍗
➡️ Working on poultry farms or live bird markets 🏪
The biggest concern is if H5N1 mutates in a way that allows it to spread efficiently between humans. This could trigger a serious public health crisis, similar to previous pandemics.
📈 Bird Flu Deaths Worldwide: Is H5N1 Becoming a Bigger Threat?
The World Health Organization (WHO) has recorded hundreds of human deaths from H5N1 bird flu over the past two decades, with a fatality rate close to 50% in confirmed cases.
The Louisiana bird flu death is part of a larger pattern of rising infections in birds and mammals across multiple countries. This raises concerns that H5N1 could spread further, increasing the risk of human infections.
Health agencies are closely monitoring mink farms, fox populations, and even seals, as the virus has been detected in these animals, raising the possibility that mammals could serve as a bridge for the virus to jump to humans.
🏥 Can H5N1 Become the Next Pandemic?
While scientists believe H5N1 is not yet capable of causing a pandemic, they are not ruling out the possibility that the virus could evolve in a way that makes it more transmissible.
If this happens, the world could face another global outbreak, similar to COVID-19 but potentially deadlier given the high mortality rate of bird flu in humans.
For now, health experts stress that early detection, biosecurity measures, and vaccine research are critical to preventing an H5N1 health crisis.
💉 Is There a Vaccine for Bird Flu?
There is no widely available bird flu vaccine for the general public, but researchers are actively developing vaccines in case the virus mutates into a more dangerous form.
Governments and pharmaceutical companies are working on emergency vaccine stockpiles, but for now, the best protection remains prevention.
🛡️ How to Stay Safe: Preventing Bird Flu Infection
While there is no immediate cause for panic, experts recommend taking the following precautions to reduce your risk of H5N1 infection:
✅ Avoid direct contact with wild birds or sick poultry 🐦
✅ Cook poultry and eggs thoroughly to kill any potential virus (165°F/74°C) 🍳
✅ Wear protective gear (gloves, masks) if working with birds 🧤
✅ Wash hands frequently with soap and warm water 🧼
✅ Report sick or dead birds to local health authorities 📞
Poultry workers, farmers, and those who work in live bird markets should take extra precautions, as they are at the highest risk of exposure.
🔥 Final Thoughts: Should You Be Worried About Bird Flu?
The H5N1 bird flu outbreak is a serious public health concern, especially with the first human death reported in Louisiana. While there is no evidence of widespread human transmission yet, experts emphasize the importance of staying informed, practicing biosecurity, and supporting vaccine development efforts.
Public health officials are working tirelessly to prevent an outbreak, but the risk remains as long as the virus continues to circulate in birds and mammals.
For now, the best course of action is to stay cautious, follow hygiene recommendations, and keep up with official health updates.
Would you like to receive real-time alerts on H5N1 bird flu and other health updates? Stay tuned for expert insights and breaking news! 🏥📢